What Is β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide?
Science • September 1, 2022 • 13min read
Highlights
- NMN has α and β forms. The α-NMN does not exist in nature, while β-NMN is the naturally-occurring form found across organisms.
- During chemical synthesis, both forms are produced, resulting in low purity of the β-NMN, which is the active form.
- Both NMN forms are nucleotides, hence they have the same three components: nicotinamide, ribose, and a phosphate group. They differ in the structural direction of the nicotinamide component.
- β-NMN is the active form because it can be recognized by the NMNAT enzyme inside our cells to produce the NAD+ molecule. On the other hand, α-NMN is not recognized by it.
- β-NMN is a widely-researched longevity molecule that may reverse aging and ameliorate aging-related diseases, as proven by clinical trials.
Introduction
NMN is now at the center stage of slowing down the aging process.
By reinstating the decreasing NAD+ levels in the body, NMN supplementation holds great promise to restore a healthy lifespan and fight age-related diseases through multiple repair and rejuvenative mechanisms.
NAD+ is a vital molecule required by hundreds of enzymes in the body to maintain health, combat diseases, and promote longevity. On top of it, NAD+ is directly correlated to age. The older a person gets, the lower his NAD+ levels will be, and the higher incidence of contracting age-related diseases.
When boosted, NAD+ ameliorates a lot of these health issues. Of all NAD+ precursors, NMN performs better overall in terms of its benefits, properties, and effects. NMN is a stable and potent NAD+ activator.
As health-driven individuals, we always want the best choice. While NMN is an amazing supplement, it exists in two chemical states – α and β forms – and only the β-NMN is useful. The α-NMN is a form that does not exist in nature and only the β-NMN is the natural form occurring in organisms with biological activities.
Since the β form of NMN is the naturally-existing form across all organisms, NMN directly refers to the β-NMN form, otherwise, it will be indicated as the other form. Similarly, in this article, NMN and β-NMN are also interchangeably used, while α-NMN is strictly written as is. Here, we talk about what is the β-NMN compound, its role in aging, and what evidence are supporting its slow aging benefits.
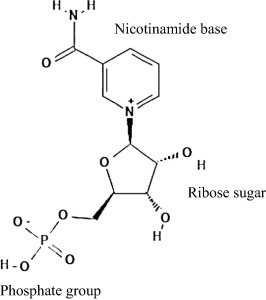
Reference structure of NMN showing the 3 chemical components as a single nucleotide. Image source
What Is β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide?
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) can exist in two forms – α and β. The β form is the natural and active form of NMN. The structures of the α and β forms vary in the direction of their nicotinamide components. The structure of β-NMN naturally results from the reaction of 3 chemical components inside the cell: a nicotinamide base (a form of vitamin B3), a phosphate group, and ribose (a sugar molecule).
Inside the cell, the enzyme that catalyzes this reaction to form the β-NMN structure is called the nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (NAMPT). In turn, β-NMN can be converted into NAD+. Hence, straightforwardly, this process is called the “NAMPT driven NAD+ biosynthesis from β-NMN” and it is a natural phenomenon inside our cells.
Meanwhile, after β-NMN is formed, another enzyme called Nicotinamide MonoNucleotide Adenylyl-Transferase (NMNAT) is the one responsible to convert it into the NAD+ molecule. Via this process, boosting NMN may drive increased NAD levels inside the cell.
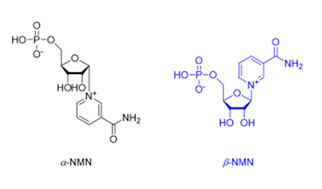
NMN has two forms. The nicotinamide group in α-NMN is at the bottom, while β-NMN’s nicotinamide component is above. Image source
The α-NMN does not exist in nature and the health implications, if ingested by the human body, are still unknown. As an unnatural compound, α-NMN is still a poorly-researched molecule. It has been used as a reagent in labs but is not exactly exploited for health applications. Besides, α-NMN cannot be used by NMNAT to produce NAD+.
β-NMN is the form that naturally exists inside our cells or other organisms, the form that is naturally found in food, and the form that is being used by our NMNAT enzyme in order to produce NAD+. Therefore, most of the NMN supplements in the market are β-NMN.
However, the chemical production of NMN supplements is not perfect and only produces low amounts of β-NMN. The production yields a mixture of β-NMN, α-NMN, and other by-products or impurities. These chemical impurities may cause harm to the human body. Hence, purification is critical to isolate β-NMN with high purity.
Therefore, it is always important to check the label of your NMN supplements or contact your suppliers to inquire about your NMN’s form and purity.
Synthesis Of β-NMN
As the most stable form of NMN, β-NMN is primarily found intracellularly in the nucleus, mitochondria, and cytoplasm and is readily available as a chemical ingredient for NAD+ production. In the human body, β-NMN is prevalent in bodily fluids, including blood and urine.
β-NMN is a component in the conversion of NAD+. NAD+ is a crucial metabolic co-enzyme or helper protein and a necessary part of a wide range of cellular processes such as aging, inflammation, DNA repair, and cell death.
However, while it is naturally produced by our cells, it declines with age and there are not enough amounts from the diet, hence, NMN is synthesized as supplements.
However, the β-NMN production is inefficient since the two forms are being produced during chemical synthesis. Thus, obtaining a pure and significant quantity of β-NMN results in heightened prices.
More cost-effective methods for producing it are needed. One emerging method for efficient β-NMN synthesis is microbial biotechnology. This technology allows the application of using microorganisms to produce specific molecules or compounds on a large scale.
In a nutshell, since our NAMPT enzyme converts the precursor molecule Nicotinamide (NAM) into β-NMN, scientists can just allow the microorganisms to express the NAMPT enzyme, feed them with NAM, and then the microorganisms will keep on producing β-NMN. This has a huge advantage since this technology can lower the costs as microorganisms are easy and cheap to cultivate.
Plus, it can allow large-scale production since microorganisms easily and exponentially multiply to billion cells that can produce the β-NMN. In addition, as long as this method is driven by NAMPT, only β-NMN can be produced, which also solves the problem of purity.
In order to overcome the high cost and purity difficulties of NMN, novel techniques and optimizations are further being researched. Numerous investigations have been consistently conducted to produce β-NMN at a low cost utilizing simple and effective biotechnological production and purification techniques.
The Role of β-NMN In Aging
Though β-NMN was initially only recognized as a source of cellular energy and a step in the biosynthesis of NAD+, the scientific community and biotechnology companies are now focusing on the slow aging properties of β-NMN. As well as several other age-related health advantages and pharmacological activities that are connected to the restoration of NAD+.
As explained above, the “NAMPT-mediated NAD+ biosynthesis from β-NMN” is a natural course inside our cells. But, this process of natural NAD+ production gets less and less efficient due to aging and age-related conditions.
Research shows that disruption is related to the impairment of mitochondrial control of oxidative phosphorylation that is involved in energy production. Therefore, by increasing the NAD+ concentration via supplementation of β-NMN, this rate of aging may be mitigated by reinvigorating the energy-generation processes of mitochondria.
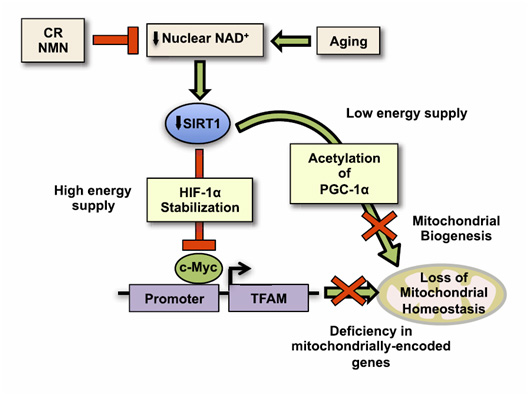
Effects of β-NMN in mitochondrial homeostasis. Image source
As a result, β-NMN has been found to have therapeutic effects on a variety of illnesses, such as age-related type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disorders such as ischemia and heart failure, obesity, and neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease, macular degeneration, and retinal degeneration.
Evidence From Animal Model Studies On The Therapeutic Effects Of β-NMN
β-NMN has shown a broad range of outstanding benefits in illness and aging of several animal models, benefiting disorders including diabetes, neurodegenerative, and cardiovascular disorders.
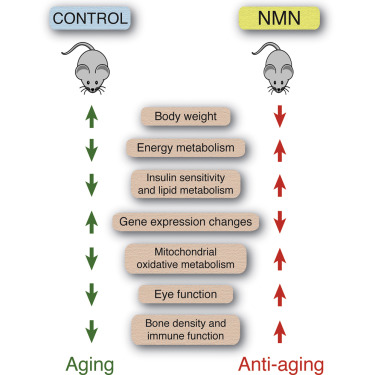
Effects of β-NMN in age-associated physiological decline in mice. Image source
Numerous investigations on rodents have shown that NAD+ content decreases with age in a variety of organs, including the pancreas, adipose tissue, skeletal muscle, liver, skin, and brain. Thus, it is expected that boosting NAD+ production with β-NMN would have considerable preventative benefits on a variety of pathophysiological alterations in the normal aging process.
In mouse tissues, β-NMN taken orally is rapidly converted to NAD+. Age-related weight gain has been prevented by β-NMN, which has also been shown to improve energy metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and visual function. β-NMN enhanced the activity and secretion of insulin in obese or diabetic mice. The mouse heart was protected by β-NMN from reperfusion damage and ischemia.
β-NMN supplementation has regenerated skeletal muscle in old mice and reduced cognitive loss in an animal model of Alzheimer’s disease by enhancing neuron survival, and energy metabolism, and lowering reactive oxygen species.
Studies also suggest that β-NMN may slow the progression of inflammaging or the development of age-associated inflammation by reducing adipose tissue inflammation. It has also been shown that older mice seem to be more receptive to β-NMN than young ones.
In short, long-term β-NMN administration studies show that β-NMN is surprisingly effective at slowing down the physiological deterioration that comes with aging in mice. It is also interesting to note that increasing NAD+ production with β-NMN has been shown to lengthen longevity in other model organisms such as yeast, flies, and worms.
Clinical Studies About β-NMN
Only recently have researchers begun investigating the effects of β-NMN in controlled, randomized clinical studies to see if the outcomes shown in cells and animal models also apply to people.
To evaluate the safety of β-NMN in people, researchers at Keio University in Japan started the first clinical trial ever in 2016. They discovered that a single oral dosage of β-NMN (between 100 and 500 mg) in ten healthy Japanese males was safe and efficiently digested without having any noticeable negative effects.
The researchers discovered no significant changes in body temperature, metabolic rates, and vision. All concentrations were well tolerated. Blood and urine sample analysis also revealed no significant changes after β-NMN ingestion.
Therefore, the researchers concluded that providing up to 500 mg of β-NMN is a safe and workable dosage for reducing age-related diseases since all of these changes were within normal limits. Importantly, previous findings also demonstrated that β-NMN is retained longer in the blood compared to NAM (another NAD precursor).
Scientists at Keio University are also carrying out phase II research to evaluate the long-term safety measures of β-NMN administration in healthy individuals, the activity, and the impact of daily administration on glucose metabolism. At Washington University, more NMN clinical studies are being conducted to investigate the impact of the supplement on cardiovascular and metabolic health indicators.
Researchers from Washington University examined how β-NMN affected prediabetic women over 55 in terms of their metabolism. Overweight or obese participants received 250 mg of β-NMN daily for ten weeks. They observed an increased insulin muscle sensitivity in prediabetic women compared to the placebo control group.
Although β-NMN intake enhanced muscles’ capacity to absorb glucose in response to insulin, it did not have the additional benefits that would say it may cure diabetes, such as lowering blood glucose levels and reducing skeletal muscle fatigue.
Another research has also been started at Hiroshima University to examine the impact of long-term oral β-NMN treatment on several hormones in healthy individuals. The University of Tokyo Hospital has also launched a new clinical trial to assess how oral β-NMN treatment affects older patients’ body composition.
Massive research efforts tapping the therapeutic potential of β-NMN to treat age-related diseases have been done. Meanwhile, clinical and safety data and further research may lead to more effective medicines based on or derived from β-NMN.
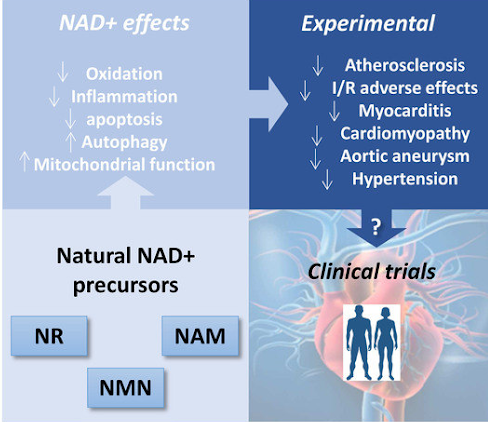
Safety and Side Effects of Taking β-NMN
Various pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and nutraceutical companies have created and marketed various β-NMN health products for slow aging. The amount of β-NMN in commercially available products ranges from 50 to 200 mg/capsule which manufacturers recommend to be taken 1-2 times a day. we still need further NMN clinical safety and efficacy studies.
In a 2020 clinical trial designed to identify safety issues in β-NMN intake, a single dose of oral β-NMN (100, 250, and 500 mg) in 10 healthy men was examined. Their clinical findings and physiological parameters found no safety issues across this range. In 2021, another clinical trial tested 250 mg/day NMN for 10 weeks in 25 prediabetes women and found beneficial effects without adverse reactions.
As purported, anything that is too much may be bad for your health. β-NMN supplements with extremely high doses, like 1000 mg and above may cause unwanted side effects. When taken at high levels, some people may experience nausea, diarrhea, flushing, stomach discomfort, and indigestion.
Nonetheless, people taking around 500 mg still have reported no significant side effects with NMN. Even at 600-1200 mg NMN per day, there is no adverse health reaction observed among middle-aged runners. However, there are few published findings on the long-term safety and therapeutic effectiveness of β-NMN’s slow aging benefits in people.
Since the necessary clinical and safety investigations have not yet been performed to define the recommended safe levels for long-term intake, the safety of these quantities still needs to be evaluated and the %DV (Daily Value) for this still needs to be established.
The %DV is FDA guidelines that recommend the percentage of daily intake of a nutrient in a serving of food. These are reference values of nutrient quantities to consume and should not be exceeded. So, recent dosage recommendations are based on currently available data and an understanding of its effects.
β-NMN should not be seen as a cure-all for the elderly since raising NAD+ levels unnecessarily might have negative consequences. As a result, the kind of age-related deficit and any other relevant health problems should be carefully considered when determining the amount and frequency of β-NMN supplementation.
For instance, animal studies show that neuron survival benefited by maintaining β-NMN at a low level. Also, β-NMN accumulation from too much intake is associated with or promotes physical nerve damage. According to reports, using less β-NMN may be safer and more effective. For instance, the brain may be more sensitive to β-NMN concentrations.
These findings demonstrated the complexity of β-NMN’s effects and the need for more research into the optimal therapeutic dosage or route of delivery. Also, as no borderline limit has been observed to drastically define the safety dosage threshold with NMN, safety issues are raised about fake suppliers of NMN products due to its booming pro-longevity popularity.
Studies show promising potential for establishing β-NMN as an evidence-based health treatment for slow aging. The generation of more toxicological and clinical data would further support its potential. Hence, β-NMN supplements are already in public and widely utilized by customers as supplementary pills for longevity. And, of course, human trials focused on safety characteristics are a top-most priority.
Closing Remarks
In sum, β-NMN is the currently available, potent NMN supplement on the market as it is the active form.
Even though the regulatory standards need to be established, there is a lot of research on its transformative health effects, with some clinical trials showing attractive safety profiles despite higher dosages, making it very promising.
With the very high health potential of this compound, backed by research evidence and consistent effects in human trials, it will not be long until it becomes a regular supplement for slow aging.