What is the Liposome and the Liposomal Drug Delivery?
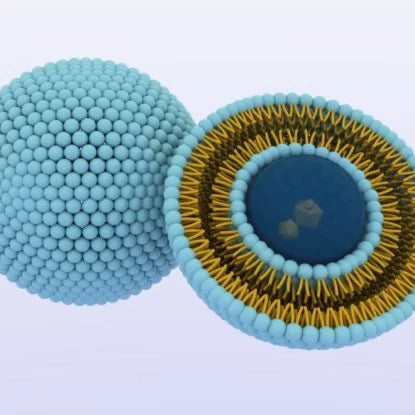
The Structure of a Liposome
Liposomes are described as sphere-shaped vesicles having a strong resemblance to the cell membrane. They are used as a very advanced technology for the effective delivery of drugs and active molecules to the desired site in the body. The name is derived from two Greek words “lipo” meaning “fat” and soma meaning “body”. Liposomes are artificial vesicles consisting of two or more concentric phospholipid bilayers. Phospholipids are a group of lipids that consist of two hydrophobic or lipophilic (fat-loving) tails and one hydrophilic (water-loving) head.
Liposomes are artificially made vesicles resembling cell membranes. They are particles with sizes ranging from 30 nanometers to several micrometers.
There are several methods [1] of liposome preparation. After preparation, liposomes are enhanced in physicochemical properties for stabilized biological characteristics.

Credit: Capsularis
Liposomes have liquid or aquose core.The phospholipid bilayers when exposed to water form a surface that is repelled by water while hydrophilic heads are attracted by water. In a single cell environment, one group of hydrophilic heads faces inside the cell while the other group of heads faces outside. Thus imitating the bilayer structure of a cell membrane.

Credit: Microfluidics
What Is The Liposomal Technology Of Drug Delivery?
The technology of liposomal drug delivery aims at improving the effectiveness of drug delivery and minimizing toxicity. The liposomal method is controlled drug delivery to the targeted site. The liposomal form of delivery can address different diseases and spots via dermal, oral, pulmonary, and parenteral routes. But the design and activity pattern of liposomes also differs for targeting different diseases and sites.
Due to their size and phospholipid bilayer characteristics, liposomes are believed to be a promising method of drug delivery. That said, they can encapsulate both hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs. There are several benefits of liposomal drug delivery [2]: liposomal drug delivery technology is believed to have high bioavailability, biocompatibility, and biodegradability. In addition, many studies have been done to decrease toxicity, and increase antitumor efficiency.
The liposome, a small cell-membrane-like vesicle [2] is made of non-toxic phospholipids and cholesterol. Cholesterol stabilizes the liposomal vesicles in a physiological environment. Hence, decreasing the probability of leakage and premature release of liposomal drugs at room temperature. The presence of cholesterol in liposomes asserts their ability to encapsulate and deliver drugs onto the targeted spot. Studies [3] show that due to these characteristics, cholesterol becomes a key ingredient in liposome formulation.
Imagine a liposome as a droplet of oil in the water [4]. Oil droplets in the water immediately repel water and form a spherical shape. However, unlike droplets of oil, liposomes, due to their bilayer properties, form a capsule that can entrap various therapeutic agents like anticancer drugs, vaccines, antimicrobials, genetic materials, proteins, and macromolecules. Liposomes carry the drug and release it to the target cells.
The technology of liposomal drug delivery is gaining popularity in modern medical and biotechnological clinics. Liposomes can build a shield around a drug and pass it through enzymes of the mouth and stomach, alkaline solutions, digestive juices as well as free radicals. Hence, liposomal drugs are resistant to oxidation and degeneration in the human body. These structural properties allow liposomes to fuse with cells and release drugs easily.

How do liposomes overcome a harsh gastrointestinal — liver pathway environment? The most remarkable advantage of liposomes is that it is easy to modify the liposomal surfaces to endow the vesicles with unique properties. To overcome harsh gastrointestinal environments like gastric acid, bile salts, and enzymes, liposome membrane composition is modulated, the surface is coated with polymers and proteins, and the liposome’s interior is thickened. These modifications provide stability and absorption of liposomes for oral drug delivery.
Another potential advantage of liposomes is their ability to contact the surfaces, thereby increasing the probability of drug absorption. This can induce specific cells to react to and absorb the liposomes. The liposome membrane surface structure is modified for particular drug targeting by changing the ionic charge on the membrane or adding particular proteins, antibodies, or immunoglobulins, for example, liposomes with specific proteins attached to membrane snag to particular cells. These targeting properties increase the affinity of liposomes to specific cells
Liposomal NAD+ Precursors To Increase NAD+ Levels
The traditional method of drug delivery shows low efficacy in absorption and delivery. So, scientists suggest a new method of using liposomal technology. The oral use of NAD+ showed significant beneficial improvements in diseases such as diabetes, Alzheimer’s, and other neurodegenerative diseases.
NAD+ is a very important molecule in the cell and provides the body with energy. They help in facilitating muscle-building processes in the body, DNA repair, and Sirtuin activation. The process of slow aging mainly depends on this key molecule. While growing old NAD+ levels drop. NAD+ supplementation can enhance the levels of NAD+in the cell.

NAD+ turns into NAD+ in tissues and has the power to suppress age-related muscle loss and weight gain. NAD+ enhances energy metabolism in the cell and prevents age-related changes in gene expression. NAD+ is also a good protector against inflammaging – accelerated aging process due to inflammation.
The liposomal NAD+ has a huge potential of reaching the focused cells aiming to reverse the aging process.
Hello100 Liposomal NAD+ contains all the advantages to boost NAD+ levels and mitigate age-related diseases.
Reference List
[1] Nkanga C.I., Bapolisi A.M., Okafor N.I., Krause R.W.M. (2019). General Perception of Liposomes: Formation, Manufacturing and Applications. In: Liposomes – Advances and Perspectives (IntechOpen). DOI: 10.5772/intechopen.84255.
Available at: https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/66369
[2] Akbarzadeh A., Rezaei-Sadabady R., Davaran S., et al. (2013). “Liposome: Classification, Preparation, and Applications.” Nanoscale Research Letters, 8(1): 102.* DOI: 10.1186/1556-276X-8-102.
Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3599573/
[3] López-Pinto J.M., González-Rodríguez M.L., Rabasco A.M. (2005). “Effect of cholesterol and ethanol on dermal delivery from DPPC liposomes.” International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 298(1): 1-12.* DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2005.02.021.
Available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0378517305001389
[4] Fattal E., Couvreur P., Dubernet C. (2004). “Smart delivery of antisense oligonucleotides by anionic pH-sensitive liposomes.” Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 56(7): 931-946.* DOI: 10.1016/j.addr.2003.10.037.
Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15066753/